A car accident head trauma can change life in seconds. Even a minor crash can cause serious brain injury that affects memory, balance, and mood. When sudden impact happens, the brain may hit the skull, leading to concussion, brain bleeding after car accident, or diffuse axonal injury. Some victims recover quickly, while others face long-term challenges like post-concussion syndrome or emotional changes. Doctors call these injuries Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI), and they range from mild to severe. Understanding the causes, warning signs, and recovery steps helps protect your brain and ensures timely treatment that can prevent lasting damage.
In most cases, head trauma after car accident is not visible right away. A person might feel fine, only to develop dizziness, confusion, or memory loss hours later. These signs often indicate deeper brain issues like Diffuse Axonal Injury (DAI) or Hematoma (Epidural, Subdural, Subarachnoid, Intracerebral). That’s why doctors recommend an immediate neurological evaluation and diagnosis by brain imaging such as MRI, CT scan, Diffusion Tensor Imaging to assess internal injuries accurately.
Car Accident Head Trauma — Causes, Symptoms, and Recovery Guide

A car accident head trauma happens when sudden force or motion makes the brain hit the skull’s inner walls. The impact can tear tiny nerve fibers, damage brain tissue, and disturb normal brain communication. This leads to cognitive problems after head injury and even long-term conditions like Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE).
Recovery depends on how severe the injury is and how soon treatment begins. Mild injuries like a Concussion may heal within weeks, while serious ones like Post-Traumatic Dementia (PTD) or Skull fracture require months of rehabilitation. The rehabilitation for head trauma includes Cognitive rehabilitation therapy, balance training, and speech recovery. Expert neurologists in U.S. rehabilitation centers use evidence-based information to track each patient’s brain damage recovery timeline for the best outcomes.
What Is Head Trauma After a Car Accident?
Head trauma after a car accident means any injury that disrupts normal brain function. It can result from a direct hit, a jolt, or even sudden deceleration. In serious collisions, the brain may twist or move violently, causing a secondary brain injury that affects memory, coordination, and emotions.
Doctors classify types of head injuries into open and closed injuries. Open injuries involve skull penetration, while closed ones occur when the brain moves inside the skull without external damage. The latter is more common in car crashes and often leads to diffuse axonal injury, contusion, or hematoma brain injury. Early medical evaluation ensures patient safety and reduces the risk of long-term disability.
Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
A Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) occurs when external mechanical force alters brain function. It’s one of the most common outcomes of car accident head trauma. The U.S. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) explains that TBI can range from mild concussions to severe, life-threatening brain damage.
There are mild vs severe TBI symptoms to recognize. Mild cases might involve temporary confusion or headache, while severe injuries can lead to unconsciousness, speech loss, and impaired mobility. Diagnosis and treatment of TBI are usually medically reviewed and verified by healthcare professionals to ensure accuracy. Hospital care for severe TBI may include surgery to reduce intracranial pressure and manage brain oxygen monitoring for stable recovery.
Common Causes of Head Trauma in Car Accidents
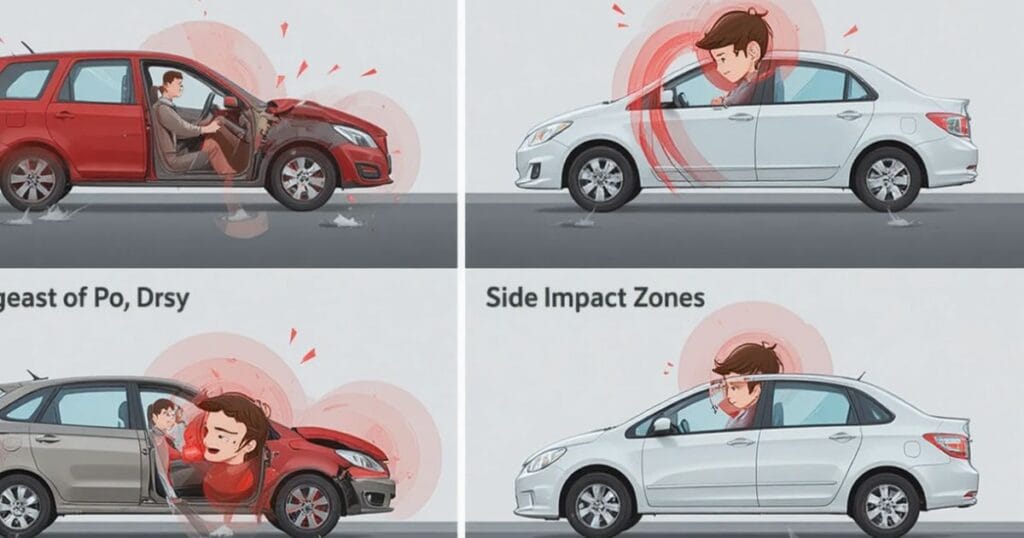
The most frequent cause of head trauma after car accident is high-speed impact. When a vehicle suddenly stops, the body keeps moving, forcing the head to strike against the dashboard, steering wheel, or window. This violent motion can result in brain bleeding after car accident and brain swelling after accident, both medical emergencies.
Even low-speed crashes can cause concussion from car crash or contusion, especially when the head jerks sharply backward and forward. Elderly head injury risk is higher because aging brains are more fragile. Statistics from CDC show that adults over 65 have a 70% higher chance of hospitalization from TBI-related injuries compared to younger adults. Quick response and diagnosis by brain imaging often prevent fatal outcomes.
Symptoms of Head Trauma After a Car Accident

Symptoms vary depending on the type and intensity of injury. Physical symptoms include headaches, dizziness, nausea, fatigue, and blurred vision. More serious cases cause vomiting, seizures, or loss of consciousness. These signs often appear within hours but can also develop days later, making it crucial to stay alert after any crash.
Cognitive symptoms are equally concerning. Victims may suffer memory loss, confusion, difficulty speaking, or trouble focusing. Emotional changes like anxiety, irritability, and depression are common signs of emotional changes after brain trauma. Ignoring these symptoms can delay recovery and increase the risk of long-term effects of head injury, including neurodegenerative diseases linked to Alzheimer’s disease and Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE).
Head Trauma Symptoms in Children
Children are more vulnerable to TBI in children because their skulls are still developing. They may not express symptoms clearly, so parents must observe for unusual behavior like excessive crying, lack of interest in play, or sleepiness. Diffuse Axonal Injury (DAI) and brain swelling / cerebral edema can develop rapidly in kids, requiring immediate medical emergency attention.
A neurology specialist often performs brain function tests and neuropsychological testing to identify hidden problems. In pediatric cases, doctors focus on patient safety and may keep children under observation for 24 hours. Clinical research funded by the Department of Defense TBI research and NIH NeuroBioBank helps improve pediatric TBI treatment guidelines in the U.S.
When to See a Doctor
You should always consult a doctor after any car accident head trauma, even if you feel fine. Some injuries, like hematoma brain injury, might not show immediate signs but can cause intracranial pressure buildup later. Delaying treatment could lead to secondary brain injury or even death.
Emergency signs include seizures, unequal pupils, continuous vomiting, and difficulty waking up. These indicate internal bleeding or brain swelling after accident. A neurology specialist will perform an immediate neurological evaluation and may admit the patient for observation. Timely intervention can prevent permanent cognitive problems after head injury and mental health after injury complications.
How Doctors Diagnose Head Trauma

Doctors use several evidence-based information methods to diagnose head trauma after car accident. A physical exam checks reflexes, coordination, and response time. If the injury seems serious, they order MRI, CT scan, Diffusion Tensor Imaging to detect internal bleeding or torn nerve fibers.
Biomarkers in blood tests also help identify traumatic brain injury causes. These tests measure proteins released from damaged brain cells. Hospitals rely on medical guidelines and trusted medical sources like the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) and NIH NeuroBioBank to ensure accurate and medically reviewed diagnoses.
Treatment Options for Car Accident Head Injuries
Treatment depends on the type and severity of head injury. For mild TBI or concussion, rest and cognitive rehabilitation therapy are usually recommended. The patient is advised to avoid screen time, alcohol, and physical activity until symptoms improve.
For severe injuries, hospital care for severe TBI may include surgery to remove blood clots, reduce intracranial pressure, or repair skull fractures. Some patients need rehabilitation programs at specialized rehabilitation centers under supervision of neurology specialists.
According to clinical research from NINDS and NIH data, early intervention improves treatment outcomes and reduces the risk of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) and neurodegenerative diseases later in life. Many hospitals participate in clinical trials such as BOOST3, TRACK TBI, and FITBIR, exploring better therapies for brain damage recovery timeline.
Recovery and Long-Term Outlook

Recovery after head trauma from a car accident varies for every individual. Some people recover within weeks, while others may take months or even years. The brain damage recovery timeline depends on injury type, age, and access to rehabilitation.
During recovery, neuroplasticity — the brain’s ability to rewire itself — plays a key role. Patients often participate in rehabilitation for head trauma programs that include physical therapy, speech therapy, and psychological counseling. Emotional healing is just as important as physical recovery, especially when dealing with mental health after injury.
Case studies show that with proper care and rehabilitation programs, even severe TBI survivors can regain independence and improve quality of life.
Complications of Untreated Head Trauma
Ignoring head trauma after a car accident can lead to serious and sometimes permanent complications. When left untreated, internal bleeding or brain swelling / cerebral edema may increase intracranial pressure, cutting off oxygen to brain tissues. This can cause secondary brain injury, further damaging vital cells.
Common complications include post-concussion syndrome, where symptoms like headaches, fatigue, and concentration problems persist for months. Others may develop chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), a degenerative brain condition often found in people with repeated head injuries.
Some victims also experience Post-Traumatic Dementia (PTD) or long-term cognitive problems after head injury, such as memory loss and poor judgment. In severe untreated cases, complications like hematoma brain injury, diffuse axonal injury, or skull fracture complications can cause lifelong disabilities or death.
Hospitals follow medical guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) to prevent such outcomes through evidence-based information, timely imaging, and proper hospital care for severe TBI.
Prevention of Head Injuries in Car Accidents

Preventing head injury in accidents starts with safety awareness and responsible driving. Always wear your seatbelt, ensure airbags function properly, and keep your headrest adjusted to support your neck.
Avoid distractions like texting while driving, and never drive under the influence of alcohol or drugs. Studies from government health agencies show that seatbelts and airbags can reduce the risk of traumatic brain injury causes by over 50%.
Parents should make sure children use age-appropriate car seats to reduce the risk of TBI in children. Elderly drivers, who face higher head injury risk, should schedule regular vision and reflex tests.
Head injury prevention tips recommended by expert neurologists also include safe driving speeds, vehicle maintenance, and using helmets when biking or riding motorcycles. These small precautions can save lives and prevent brain bleeding after car accident or concussion from car crash.
Legal Aspects of Head Trauma After an Accident
In the United States, victims of car accident head trauma have legal rights to seek compensation. Medical expenses, lost wages, rehabilitation costs, and emotional suffering can all be part of a personal injury claim.
Documentation is essential — medical reports, diagnosis by brain imaging, and hospital records can help prove the seriousness of your injury. Working with a lawyer experienced in brain injury cases can ensure fair compensation and protect your patient safety rights.
Some cases involve long-term patient care needs that extend for years. Courts often rely on clinical research, verified by healthcare professionals, to estimate future costs. Victims should act quickly, as each state has its own statute of limitations for filing injury claims.
Living With a Traumatic Brain Injury
Life after a Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) can be challenging, but recovery and adaptation are possible. Many people experience changes in memory, attention, and mood. Cognitive rehabilitation therapy and mental health after injury programs help patients manage these challenges and regain independence.
Support groups, rehabilitation centers, and neurology specialists offer customized programs based on each patient’s needs. These may include speech therapy, occupational therapy, and emotional counseling.
Families also play a key role in recovery by providing emotional support and ensuring medication adherence. Regular follow-up appointments with a neurologist and neuropsychological testing can track improvement and prevent complications like neurodegenerative diseases.
The road to living with TBI requires patience and a strong support system, but many survivors return to fulfilling lives through rehabilitation programs and modern medical care.
Latest Research and Medical Advances
Medical science continues to make progress in diagnosing and treating head trauma after car accident. Clinical research funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and Department of Defense TBI research projects is discovering new therapies and better diagnostic tools.
Programs like BOOST3, TRACK TBI, and FITBIR focus on monitoring brain oxygen levels, improving biomarker detection, and studying neuroplasticity to enhance recovery. Researchers are also exploring the role of the blood-brain barrier and brain tissue donation through the NIH NeuroBioBank to understand long-term outcomes.
MRI, CT scan, and Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) now provide clearer views of diffuse axonal injury, hematoma, and contusion patterns, improving early diagnosis. Clinical trial participation allows patients to access cutting-edge treatments that may reduce long-term effects of head injury and accelerate recovery timelines.
These advancements ensure evidence-based information and treatment outcomes supported by trusted medical sources and data from government health agencies like CDC and NINDS.
Final Thoughts
The Road to Recovery
Recovering from car accident head trauma can be a long journey filled with physical, emotional, and cognitive challenges. However, with expert neurologists, early diagnosis by brain imaging, and proper rehabilitation programs, most patients can regain function and rebuild their lives.
Medically reviewed treatment strategies and rehabilitation centers across the USA provide hope and healing to thousands every year. The key is never to ignore early symptoms, seek medical emergency care immediately, and follow evidence-based information from trusted medical sources.
As awareness, research, and technology continue to grow through clinical trials, NINDS and NIH data, and government health initiatives, the future of head trauma recovery looks brighter than ever. With patience, support, and proper care, the road to recovery is always possible — even after the most severe car accident head trauma.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article on Car Accident Head Trauma is for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended to serve as medical advice or replace consultation with a qualified healthcare professional. Always seek immediate medical attention if you or someone you know experiences a head injury, concussion, or any neurological symptoms after a car accident.
While this article is based on evidence-based information, trusted medical sources, and data from government health agencies such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), readers should not rely solely on online material for diagnosis or treatment.
Every case of traumatic brain injury (TBI) or head trauma after a car accident is unique. Only expert neurologists and licensed medical professionals can provide accurate diagnosis and treatment tailored to individual needs.
If legal issues arise due to an accident or injury, consult a qualified personal injury attorney for advice about your rights and compensation options.
The author and publisher of this content make no representations or warranties regarding the accuracy, applicability, or completeness of the information provided. Use of this website and its content is at your own risk.
FAQS
| Question | Answer |
| How to treat head trauma? | Immediate medical evaluation is vital. Treatment may include rest, medications, surgery, and rehabilitation for head trauma depending on the severity. |
| How long after hitting your head can concussion symptoms start? | Concussion symptoms can appear within minutes or up to 48 hours after the injury. Some signs may even develop slowly over several days. |
| What are the symptoms of a head injury after a car accident? | Common symptoms include headache, dizziness, confusion, nausea, blurred vision, and sometimes memory loss or fatigue. |
| What is the protocol for head trauma? | The standard protocol includes neurological evaluation, MRI or CT scan, monitoring for intracranial pressure, and rest with gradual recovery. |
| Can the brain heal from head trauma? | The brain can partially heal through neuroplasticity, but recovery depends on the type and severity of injury and timely medical care. |
| How to know if head trauma is serious? | Severe head trauma causes loss of consciousness, vomiting, unequal pupils, seizures, or confusion — seek emergency medical attention immediately. |

Muhammad Maaz, founder of InjuyCrashGuide.com — sharing simple, real-life accident and insurance guidance to help people stay informed and protected.