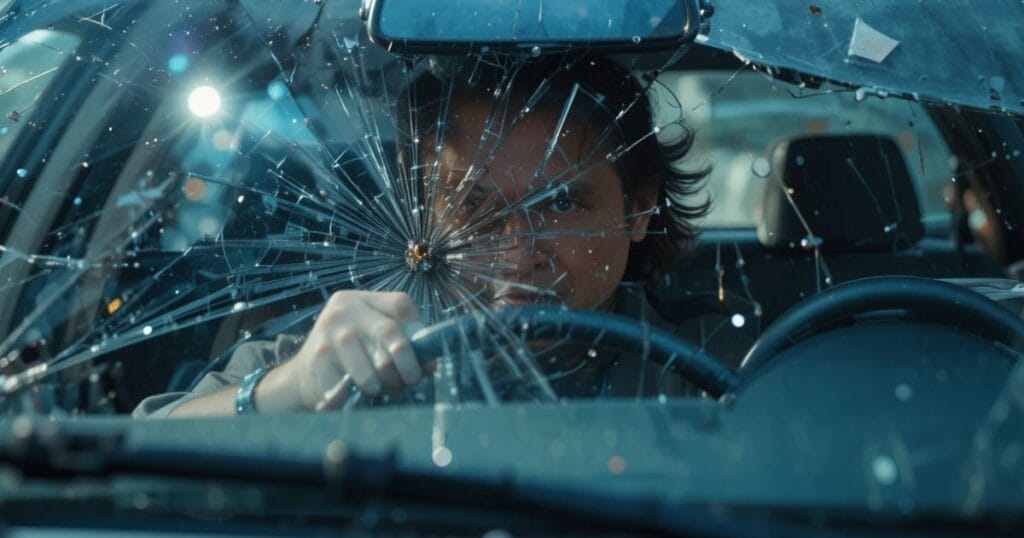
Suffering a head hit windshield in car accident is one of the most dangerous forms of impact because the force travels directly to the skull and brain within milliseconds. Even if there is no visible bleeding, the risk of traumatic brain injury after car accident remains extremely high. Many victims walk away thinking they are fine, only to develop symptoms of head trauma hours or days later. A head slammed into windshield injuries can lead to confusion, dizziness, memory loss, or even unconsciousness. Understanding what happens if your head hits the windshield is critical for protecting your health and legal rights immediately after the crash.
This article explains in detail what happens if your head hits the windshield, how serious it can be medically AND legally, what immediate steps after hitting head in crash you must take, what kind of scan detects brain injury, when to go to emergency room for head trauma, and how early treatment improves recovery and helps establish documented medical evidence for future insurance or legal claims.
What Does It Mean When Your Head Hits the Windshield in a Car Accident?

When the head slammed into windshield injuries occur, it means the body was thrown forward with enough momentum to break past the seatbelt’s restraint force or that the seatbelt was not worn correctly. This type of impact generates intense brain swelling and intracranial pressure, even if there is no visible damage on the skin. Many first-time accident head hit windshield in car accident impact is not only a blow to the outer skull — it can trigger closed head injury vs open head injury depending on whether the skull cracks or glass penetrates the scalp. Closed head injuries can be even more dangerous, as swelling happens inside — silent but deadly — without external warning signs.
How Head Impacts Happen During a Car Crash

A head hit windshield in car accident usually occurs during frontal or angle collisions, when the driver or passenger’s upper body is violently thrown forward before the seatbelt or airbag fully restrains them. In rear-end crashes, the reverse motion can cause severe whiplash and brain injury connection, where the brain ricochets inside the skull, causing coup and contrecoup brain injury without ever touching the windshield.
Even if airbags deploy, they do not always prevent head slammed into windshield injuries — especially if the seatbelt is worn incorrectly, too loosely, or if the airbag fails or deploys too late. This means even a crash at 30 mph can generate deadly brain force equal to a 10-foot concrete fall.
Immediate Risks If the Head Slams Into the Windshield

The first 60 minutes after a head hit windshield in car accident are medically critical. Physicians call this window the “golden hour” because emergency medical attention required during this time can prevent life-threatening brain damage warning. Swelling inside the brain can silently progress, pushing against the skull and disrupting oxygen supply.
Many victims feel “normal” and choose to go home — and this is where untreated brain injury complications begin. The danger is not always pain — it is secondary brain swelling after accident, which can cause sudden collapse hours later even during sleep.
Visible vs. Hidden Head Injuries After Impact
In a closed head injury, the skull remains intact — no blood, no cut, no fracture. This is what makes it extremely misleading. Internal bleeding, post-concussion syndrome after crash, and microscopic axonal tearing may be happening while everything looks normal outside.
In an open head injury, there may be broken glass impact, skull fractures, heavy bleeding, or visible deformity. These get treated fast — but statistically, hidden brain injuries are often deadlier because they are ignored. This is why experts say: never trust how you feel — only trust medical imaging.
Concussion and Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Explained
A concussion is not “just a headache.” It is a form of traumatic brain injury after car accident, where the brain’s normal electrical communication is disrupted. Symptoms may include confusion, delayed reaction, emotional imbalance, or is dizziness normal after head injury — yes, it is.
What many Americans don’t know is that mild traumatic brain injury does not always involve loss of consciousness in car accident. You can remain awake, talking, and still be at risk of medically verified symptoms hours later — including emotional meltdown, fainting, memory loss, or sudden vomiting.
Serious Head Injuries That Can Occur on Windshield Impact
A strong head hit windshield in car accident impact can lead to far more severe injuries than a mild concussion. One of the most dangerous is diffuse axonal injury, where the brain’s nerve fibers stretch and tear due to extreme rotational force. Victims can slip into a coma without warning. Another serious condition is brain swelling and intracranial pressure, which can rise rapidly and restrict oxygen flow — a life-critical emergency.
Coup and contrecoup brain injury occurs when the brain is slammed forward into the skull, then rebounds backward, hitting the opposite side. This dual-trauma pattern often affects memory, emotional control, speech, and balance. Without diagnosed through CT scan or MRI, this injury may not show noticeable symptoms at first — but permanent risk of permanent cognitive disability can follow.
Warning Symptoms That Should Never Be Ignored

Even if someone feels “okay,” warning signs can develop minutes, hours, or even days later. Common symptoms of head trauma include confusion, blurred vision, nausea, speech difficulty, sudden sleepiness, or dramatic mood swings. These are medically verified symptoms — not to be ignored or monitored casually at home.
If any moment feels “not normal” — even slight disorientation, sudden emotional breakdown, or is dizziness normal after head injury — it must be treated as a life-threatening brain damage warning. Doctors warn that once swelling begins rapidly inside the skull, the brain can become dangerously compressed in under 30 minutes.
Can You Have a Brain Injury Without External Bleeding?
Yes — absolutely. In fact, the majority of traumatic brain injury after car accident cases in the U.S. involve no visible external wound. This is called a closed head injury, where damage is internal — bleeding, swelling, or torn neural tissues all happening inside the skull. In legal and medical cases, this becomes a major defense error when victims say “I didn’t bleed, so I didn’t go.”
Only diagnosed through CT scan or MRI can confirm exactly what is happening inside. Doctors strongly advise against waiting — especially for people feeling only mild headaches or pressure. Internal brain injuries don’t need wounds to be fatal.
Delayed or Late-Appearing Head Injury Symptoms
Many Americans make the mistake of thinking “If something was wrong, I would feel it immediately.” That belief has led to thousands of delayed fatalities. How long does brain injury take to show symptoms? In many cases — 12 to 72 hours. Sometimes even weeks, especially with post-concussion syndrome after crash.
Common delayed symptoms after car accident include memory fog, irritability, visual distortions, anxiety attacks, fatigue, speech difficulty, or sudden collapse. A person may function fine at work or school — then crash days later. This is why medically evaluated by neurologist follow-up exams are essential even if initial checkups look normal.
What to Do Immediately After Your Head Hits the Windshield
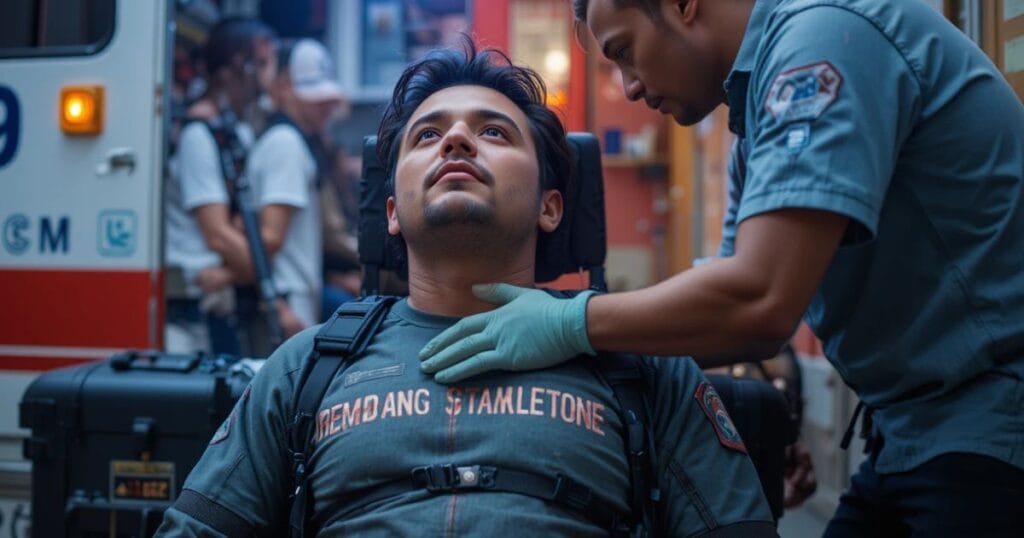

The first few minutes after a head hit windshield in car accident can decide life or death — even if the impact did not cause bleeding or loss of consciousness. The absolute first step is to remain still and avoid sudden movement. Neck and spinal injuries often occur together with head slammed into windshield injuries, and moving too fast can worsen internal trauma. Next, do not claim that you are “fine.” Instead, immediate steps after hitting head in crash include calling 911, requesting emergency medical attention required, and reporting that the head took direct impact — not just general collision. This creates documented medical evidence right from the scene, which is critical not only for survival but also for insurance and legal protection later.
Avoid painkillers such as ibuprofen or aspirin before being examined — these may increase brain bleeding risks if internal hemorrhaging has started. A calm person who delays treatment can fall unconscious within the hour due to secondary brain swelling after accident. That is why medical response must always happen before self-assessment, driving home, or talking to the other party about settlement. Nothing is more urgent than brain safety.
Medical Tests Used to Diagnose Head Injuries
In U.S. hospitals, the most reliable what kind of scan detects brain injury is either diagnosed through CT scan or MRI, depending on the initial symptoms. A CT scan is often used within the first hour to detect skull fractures, blood clots, and brain swelling and intracranial pressure. An MRI goes deeper — identifying subtle coup and contrecoup brain injury, torn neural tissues, or early bleeding that cannot yet be seen externally. Patients are often kept under observation for several hours even if initial results look normal. This is because how long does brain injury take to show symptoms varies for each individual — and doctors fully understand that internal damage can expand silently.
If needed, a neurological exam is ordered by a medically evaluated by neurologist, checking pupil response, memory recall, speech accuracy, balance, and reaction reflexes. This step is crucial since even mild whiplash and brain injury connection can interrupt cognitive function. A normal-looking face can still hide a life-threatening brain damage warning — something only medical imaging can reveal with certainty.
Short-Term Effects and Recovery Timeline
Right after a head hit windshield in car accident, short-term symptoms may appear within minutes, hours, or even a full day later. Some people experience headaches, confusion, light sensitivity, nausea, or brief loss of consciousness in car accident, while others may just feel “off” without obvious pain. Even these light symptoms could indicate traumatic brain injury after car accident, which means the brain is struggling to stabilize itself. Doctors closely monitor movement ability, response time, and medically verified symptoms like delayed speech or unstable balance. A mild injury may start improving within days — but must never be ignored during the first 72 hours, which are medically considered “risk-critical.”
mild vs severe head injury recovery time varies depending on brain swelling or internal bruising. Mild impact injuries can improve in 2–6 weeks, but moderate cases often include post-concussion syndrome after crash, where dizziness, anxiety, sleep issues, or memory lapses continue for months. Severe injuries take longer — sometimes beyond a year — especially when early treatment improves recovery was delayed. During this time, frequent neurological check-ups are required to ensure no untreated brain injury complications develop later.
Long-Term Complications of Head Impact Injuries
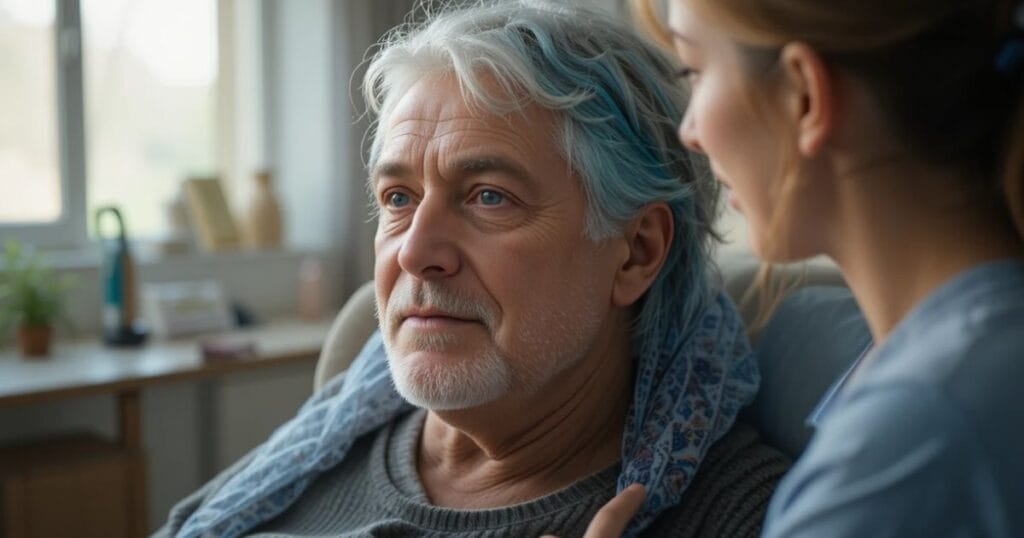

The long-term danger is not just pain — it is risk of permanent cognitive disability. A person who looked healthy in the first few hours can develop long-term neurological complications weeks later if secondary brain swelling after accident was not treated on time. Memory gaps, emotional instability, speech issues, sleeping disorders, or slower decision-making can start appearing later — making it difficult to perform normal work or daily responsibilities. Brain changes don’t always heal completely, which is why many U.S. cases end with lifelong medical follow-ups.
Severe injuries may affect learning ability, movement coordination, or mental focus permanently. Some people also suffer mood disorders triggered by damaged brain cells related to emotion regulation. This is why CDC traumatic brain injury statistics strongly emphasize the importance of detecting even “mild-looking” cases early. Many Americans who ignored slight dizziness or confusion ended up with unexpected long-term loss of independence.
When to Visit the Emergency Room Urgently
You should never delay going to the ER if any signs you need to see a doctor after head injury appear — even if hours have passed since the impact. Warning signals include confusion, blurred vision, difficulty speaking, numbness in hands or feet, extreme fatigue, or rapidly worsening headache. If vomiting starts, if is dizziness normal after head injury becomes a repeating pattern, or if the person suddenly becomes unusually quiet or agitated — these are strong life-threatening brain damage warning signs. Immediate ER transport is essential in all these scenarios.
Another signal is fluid leaking from the nose or ear — which may be cerebrospinal fluid — a direct sign of internal skull breach. In simple words, if behavior, speech, or awareness changes in any way after your head slammed into windshield injuries, treat it as an emergency. The golden rule used by U.S. trauma doctors is clear — when to go to emergency room for head trauma is before things look dangerous, not after.
First Aid Precautions Before Medical Help Arrives
First aid must be calm and controlled. Make the injured person sit or lie safely with head slightly elevated to reduce brain swelling and intracranial pressure, but do not move their neck or spine. Never apply pressure to a visible bump, never shake or force them to stay awake, and never give food, water, or medication until cleared by professionals. If consciousness drops — check pulse and breathing but avoid tilting the head aggressively.
The priority before hospital arrival is simply stability, not treatment. The goal is to prevent additional injury while waiting for emergency medical attention required. If multiple injuries exist — head trauma must still be considered the most critical. Internal brain pressure can rise with each passing minute — and nothing is more important than getting the victim transported safely and fast.
How to Prevent Head Injuries in Future Car Accidents
Prevention begins before the crash ever happens. Always wear a correctly fitted seatbelt, not loosely across the body, and never recline your seat back too far — this keeps your head from violently flying forward in a collision. Modern vehicles with airbags and reinforced windshield protection reduce head impact risk dramatically when passengers are sitting upright in the correct driving posture. Avoid placing heavy or loose objects on the dashboard or front panel, as these can become deadly projectiles on impact.
Choosing safer vehicles also matters. Cars equipped with advanced collision warning systems, lane-departure alerts, automatic braking, and headrest protection have proven to reduce fatal or severe impact injuries. Driving distraction-free — with no texting or aggressive speeding — remains one of the strongest ways to prevent head hit windshield in car accident scenarios entirely. Prevention is not luck — it is discipline behind the wheel.
Most Common Mistakes People Make After a Head Impact
The biggest mistake is assuming everything is fine because there is no visible bleeding. Can you have a brain injury without external bleeding? — absolutely yes. Another dangerous mistake is going to sleep right after impact without medical clearance, believing rest will fix the problem. This can quickly turn fatal if secondary brain swelling after accident begins silently in the brain. Delaying medical help “to see if symptoms improve later” is another life-threatening error.
People also fail to record symptoms immediately — losing the chance to build documented medical evidence later, especially in legal or insurance claims. Some even consume painkillers like ibuprofen right after the injury — which is very risky if internal brain bleeding exists. Panic is harmful — but ignoring medical urgency is worse. The human brain can deteriorate without warning — and early caution is everything.
What Happens If You Delay Medical Treatment After a Head-On Collision?
Delaying care after your head hit windshield in car accident raises real danger. Internal bleeding can expand slowly while you feel fine, and secondary brain swelling after accident can compress vital areas. A short delay can change a treatable condition into a permanent deficit or a life-threatening emergency.
Delays also weaken your documented medical evidence later. Emergency notes, scans, and early symptom records matter for medical follow-up and insurance claims. If you hesitate, symptoms may worsen and untreated brain injury complications become harder to reverse.
Can You Develop a Delayed Brain Injury Without Immediate Symptoms?
Yes — many victims show no immediate signs after their head slammed into windshield injuries. Microscopic bleeding or axonal stretching can remain silent for hours or days, then trigger memory loss or mood changes. This is why how long does brain injury take to show symptoms varies widely.
Delayed symptoms include dizziness, increased sleepiness, and slowed thinking. These common delayed symptoms after car accident can mimic stress or fatigue, so get checked. A timely CT or MRI catches hidden damage and helps a medically evaluated by neurologist plan proper care.
How Long Does Post-Accident Head Trauma Typically Last?
Recovery depends on severity. Mild cases often improve in weeks, while moderate injuries may take months. mild vs severe head injury recovery time varies, and ongoing symptoms may signal post-concussion syndrome after crash that lasts beyond three months.
You should expect frequent follow-ups. Therapies, cognitive rest, and graded return to activity shorten recovery. Early intervention matters, and early treatment improves recovery chances significantly.
Are Headaches After a Car Accident a Sign of Internal Bleeding?
A headache alone does not prove internal bleeding, but it can be a warning. Severe, worsening, or sudden-onset headaches after your head hit windshield in car accident require urgent imaging because they might signal a bleed or growing pressure.
Also watch for nausea, vomiting, or confusion with headache. These paired signs heighten concern for brain swelling and intracranial pressure, and they justify immediate ER evaluation and diagnosed through CT scan or MRI to rule out dangerous causes.
What Warning Signs Indicate Your Head Injury Is an Emergency?
Seek immediate care for slurred speech, repeated vomiting, unequal pupils, seizures, or sudden behavior change. These are clear life-threatening brain damage warning signs and need ambulance transport. Loss of coordination and progressive confusion also demand urgent attention.
If fluid leaks from the nose or ear, or if you experience prolonged loss of consciousness in car accident, treat the situation as critical. Rapid medical action often prevents catastrophic outcomes and secures documented medical evidence for later care and insurance steps.
How Do Doctors Diagnose Hidden Brain Injuries After a Car Crash?
Doctors begin with neurological exams, checking your speech, reflexes, memory, and eye movements. If your head hit windshield in car accident, they may immediately order a CT scan to check for brain bleeding, especially within the first few hours. CT scans are fast and ideal for detecting skull fractures and active bleeding.
If symptoms progress or persist, an MRI after head trauma accident might be ordered. MRI scans detect more subtle injuries like nerve fiber damage or post-concussion brain changes that CT might miss. In some cases, neurocognitive tests are used to evaluate memory, focus, and processing speed for silent injuries.
What Is the Difference Between a Mild and Severe Head Injury?
A mild head injury (concussion) may cause dizziness, headache, blurred vision, fatigue, or mental fog — usually without prolonged unconsciousness. Recovery often happens within weeks if treated correctly.
A severe head injury, however, may involve extended loss of consciousness, seizures, bleeding, or fluid leakage from ears/nose. These cases pose high risk of permanent neurological damage or death if untreated. Severe injuries require emergency hospitalization and intensive neurological monitoring.
What Medical Treatments Are Given for Head Injuries After a Car Accident?
Treatment depends on injury severity. Mild cases may only require brain rest, pain management, and follow-up monitoring. But if doctors detect bleeding, swelling, or skull fracture, emergency steps include:
Medication to reduce brain swelling and intracranial pressure
Oxygen support or intubation for low brain oxygen levels
Emergency brain surgery to remove clots or relieve pressure
Observation under 24–72 hours of neurological monitoring
The sooner treatment begins, the higher the chance of full neurological recovery.
When Should You See a Neurologist or Brain Injury Specialist?
If your headache after car accident didn’t hit head persists for more than a few days, or if you feel foggy, confused, or emotionally unstable — see a neurological specialist immediately. This includes symptoms like:
Memory loss or forgetfulness
Difficulty concentrating on simple tasks
Sudden mood swings or irritability
Light and sound sensitivity
Sleep disturbances
These could indicate post-concussion syndrome or delayed brain trauma that requires specialized management — not just basic pain medication.
Can Head Injuries Cause Memory Loss or Behavioral Changes Later?
Yes — even mild head injuries can trigger delayed cognitive or emotional changes, especially if left untreated. Some victims report:
Forgetting conversations or appointments
Slow response time in thinking or speaking
Sudden anxiety, panic, or depression
Personality changes noticed by family or friends
This is often linked to frontal lobe or temporal lobe impact — the areas controlling emotions, memory, and decision-making. Immediate evaluation and therapy can prevent long-term brain complications.
How Long Does It Take to Fully Recover from a Head Impact in a Car Accident?
Recovery time depends entirely on how severe the brain injury is. A mild concussion may heal in 2 to 4 weeks with strict rest and no screen exposure or heavy thinking tasks. However, moderate to severe head injuries can take months or even years to recover — and in some cases, full recovery may never happen. This is why early medical treatment is critical.
Doctors closely monitor recovery using follow-up neurological exams. Many people don’t realize that secondary brain swelling after accident can occur days later — causing sudden and dangerous deterioration, even if they felt “normal” at first. Never assume you are fine just because you can walk and talk right after the accident.
Can You File a Legal Claim If Your Head Hit the Windshield in a Car Accident?
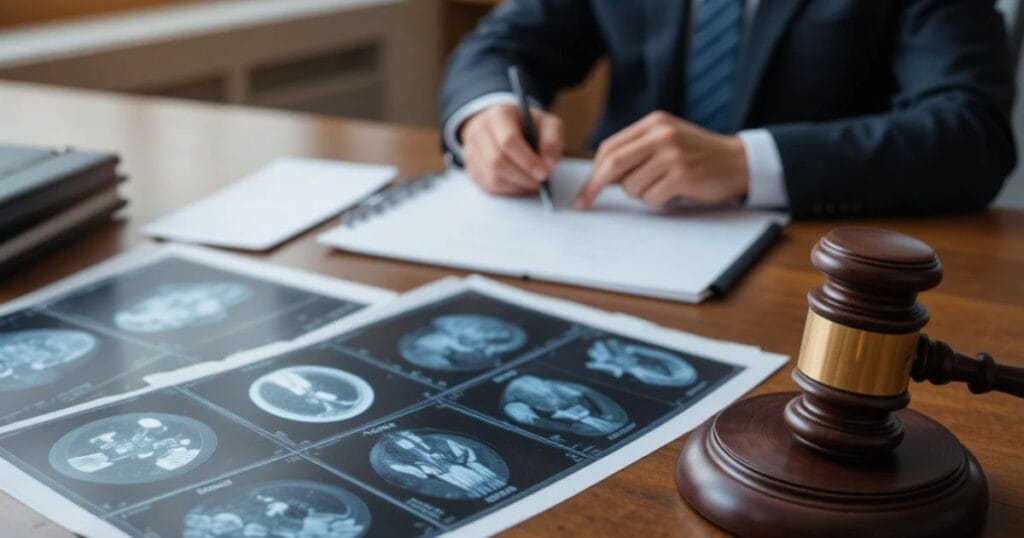

Yes — if your head hit windshield in car accident, you may have legal rights to compensation for medical costs, ongoing treatment, lost wages, and pain or emotional suffering. Head injuries are taken very seriously in U.S. personal injury law, especially because they may lead to lifelong consequences.
Attorneys often build your case using documented medical evidence, such as hospital records, CT/MRI results, neurologist reports, and proof of cognitive impairment. If another driver was negligent — distracted driving, speeding, drunk driving — your compensation claim becomes even stronger.
How Can You Protect Your Legal Rights After a Head Injury Accident?
The biggest legal mistake people make is not going to the hospital immediately or downplaying symptoms. Insurance companies may later deny claims, arguing that your injury is unrelated or “not serious enough.” You should always:
Get medically verified symptoms recorded immediately
Do not give casual verbal statements to insurance companies
Consult a car accident attorney before accepting any settlement
Keep all hospital documents, test reports, and expense receipts
This ensures that documented proof exists if delayed symptoms appear later — which is common with head trauma cases.
Why Immediate Medical Attention Helps Both Health and Legal Case
Emergency medical attention required does not just protect your brain — it protects your future. Doctors create a time-stamped medical record that proves your injury happened from the crash, not from something later. This is extremely important in U.S. insurance and legal claims.
Also, early treatment improves recovery. The brain is highly sensitive to delayed treatment. What could have been a mild injury may become a severe one if oxygen flow, swelling, or internal bleeding is not controlled in time. Never delay — your brain does not give second chances.
Conclusion
Experiencing a head hit windshield in car accident is never something to ignore — even if you feel “fine” afterward. Head and brain injuries are often silent at first but can worsen quickly due to secondary brain swelling, delayed bleeding, or rising intracranial pressure. Many survivors later regret not seeking emergency care immediately.
Your first priority must always be medical — not legal, not insurance.
Go to a hospital, get diagnosed through CT scan or MRI, and ensure your condition is medically evaluated by neurologist as soon as possible. This protects both your life and legal rights.
Key reminders before we close:
Never wait to “see if it gets better.” Brain injuries do not heal with luck — they heal with timely treatment.
Even mild symptoms like dizziness or confusion are serious. Wondering “is dizziness normal after head injury”? No — it’s a medical warning.
Documented medical evidence is the strongest protection for both your health and you injury claim.
Untreated brain injury complications can cause permanent cognitive disability — including memory loss, personality change, or even coma.
Life-threatening brain damage warning signs can appear hours or even days later — not just at the crash scene.
In simple words:
Your brain is irreplaceable. One smart decision today can prevent a lifetime of regret. Always treat any head impact in a car accident as an emergency — even if you walked away on your own.
FAQS
| Question | Answer |
| What happens if your head hits the windshield in a car accident? | It can cause concussion, skull fracture, brain bleeding, or internal swelling even with no external wounds. Immediate medical evaluation is necessary. |
| Can you have a brain injury without visible bleeding? | Yes. This is called a closed head injury — bleeding or swelling can occur inside the skull, invisible from the outside. |
| How long does brain injury take to show symptoms? | Some symptoms appear instantly, but others may take 24 hours to 3 weeks — this is known as delayed symptoms after car accident. |
| Is dizziness normal after head injury? | No — dizziness is a neurological warning sign. It may indicate brain swelling, concussion, or inner ear injury. |
| When to go to emergency room for head trauma? | If you experience vomiting, confusion, blurry vision, fainting, memory loss, severe headache, or fluid from nose/ears, go immediately. |
| What kind of scan detects brain injury? | CT scan detects bleeding or fractures immediately. MRI detects deeper brain injuries and post-concussion damage more accurately. |
| Can whiplash cause brain injury without head hitting anything? | Yes — rapid back-and-forth neck motion can cause coup and contrecoup brain injury, similar to hitting the head. |
| Can symptoms come back weeks later? | Yes, post-concussion syndrome after crash may appear weeks or months later, causing headaches, mood changes, and memory problems. |
| Can delaying treatment affect legal compensation? | Absolutely — insurance companies may deny claims without documented medical evidence within 24–72 hours after accident. |
| Can a mild head injury become worse over time? | Yes. Secondary brain swelling after accident can turn a mild injury into a life-threatening emergency if untreated. |
| How do I know if my head is ok after hitting it? | If you have no dizziness, nausea, vision changes, confusion, or headache — and symptoms don’t worsen within hours — it’s likely mild, but still monitor closely. |
| What to do if you hit your head in a car accident? | Stop moving, stay calm, avoid sleeping, and get medically checked immediately — even if symptoms seem minor. |
| What is the 4 hour rule for head injury? | You must be monitored for at least 4 hours after impact to watch for delayed symptoms like vomiting, confusion, or drowsiness. |
| What is the average payout for a head injury? | Minor head injuries may settle between $20,000–$80,000, while severe cases can exceed $500,000 or more. |
| What is a good settlement for a car accident? | A fair settlement covers all medical costs, future treatment, lost wages, and pain and suffering — usually $15,000 to well over $100,000+. |
| What is the hardest injury to prove? | Mild traumatic brain injuries and emotional or cognitive damage are hardest to prove because they often lack visible evidence. |
Explore mor e Article
Headache After Car Accident Didn’t Hit Head?
How to Deal with Car Insurance Adjusters
How to Deal with Insurance Adjuster (Complete Guide 2025)

Muhammad Maaz, founder of InjuyCrashGuide.com — sharing simple, real-life accident and insurance guidance to help people stay informed and protected.



